This article was published in Scientific American’s former blog network and reflects the views of the author, not necessarily those of Scientific American
In this episode of our podcast My Favorite Theorem, my cohost Kevin Knudson and I were happy to talk with Jana Rodriguez Hertz from the Southern University of Science and Technology in Shenzhen, China. You can listen to the episode here or on kpknudson.com, where there is also a transcript.
Dr. Rodriguez Hertz chose to talk about Stephen Smale’s horseshoe map on the show. But first she talked about noodles. She took this video of a cook making noodles at her campus canteen. The cook stretches the noodles, folds them over on themselves, and stretches them again, repeating the steps several times before throwing the noodles in the pot.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
This process is a lot like the horseshoe map. The horseshoe map is a function from a square to itself. First, you deform the square by squishing it in one direction and stretching in the other direction so you have a long, narrow strip that’s the same area as the original square. Now you fold the strip into a horseshoe shape so 1/3 of it is in 1/3 of a square, 1/3 is in another 1/3 of a square, and the middle 1/3 forms the bendy part of the horseshoe. For the purposes of this map, we’ll throw away that middle third, the part that doesn’t land back in the original square. In the diagram below, the left 1/3 of the square has been mapped to the bottom 1/3 of the square and the right 1/3 of the square to the top 1/3 of the square. (On the podcast episode, Dr. Rodriguez Hertz describes a rotated version of the map in this diagram. The idea is the same.)
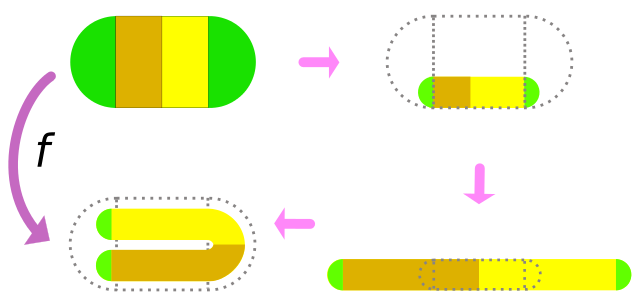
A diagram of the Smale horseshoe map. Credit: SyntaxError55 Wikimedia(CC BY-SA 3.0)
That map isn’t so impressive if you only do it once, but if you perform that transformation once and then perform it again and again, like the cook making noodles, you start to get something cool, and that cool behavior is Dr. Rodriguez Hertz’s favorite theorem. Most points are eventually discarded because they get stuck in the bendy part of the horseshoe at some time, but the parts that stay in the square get stretched into a noodly version of the Cantor set. (Read more about the Cantor set here.)

Seven iterations of the infinite process that creates the Cantor set. Credit: 127rect Wikimedia
You can also imagine running the map in reverse. Instead of the top 1/3 of the square going to the left 1/3 and the bottom going to the right, you get the left 1/3 of the square going to the top 1/3 and the right 1/3 going to the bottom 1/3. You can ask whether any points will remain in the square forever, whether you go forwards or backwards, and there are some. The points that stay forever, also called the invariant set, form a space called Cantor dust.

Cantor dust is the product of two Cantor sets the same way a plane is the product of two lines. Credit: Solkoll Wikimedia
As Dr. Rodriguez Hertz describes, the horseshoe map is a vivid illustration of chaotic behavior arising from a fairly simple system. One of the hallmarks of chaos is that a chaotic system is very sensitive to initial conditions, and that holds for the horseshoe map. No matter how close two points are to each other, eventually their behavior will be completely different. In fact, as she mentioned, you can actually describe a point completely and uniquely by noting where it goes under iteration by this map, an idea related to something called symbolic dynamics. Dr. Rodriguez Hertz also mentioned a map called the tent map, another simple system with chaotic behavior. You can read more about it here.
She also mentioned the horseshoe map’s connection to an area called symbolic dynamics. The basic idea of symbolic dynamics is that you can encode the behavior of points in a system that undergoes a transformation using a finite number of letters or numbers. In the case of the horseshoe map, she describes how each point in the invariant set can be described by a sequence of 0s and 1s, which represent which part of the set it is in at every step, both forwards and backwards.
.JPG?w=450)
Dr. Rodriguez Hertz with Stephen Smale, the eponym of Smale's horseshoe map. Credit: Jana Rodriguez Hertz
In each episode of the podcast, we ask our guest to pair their theorem with something. Dr. Rodriguez Hertz, who was born in Argentina and worked in Uruguay for many years before moving to China, riffed on the idea that a point in the horseshoe map is completely determined by its path and talked about how that idea resonates in her life. You’ll have to listen to the episode to get the full story. I thought it was interesting that both she and Ami Radunskaya, who talked with us about the Birkhoff ergodic theorem, also in the field of dynamical systems, waxed philosophical about how their theorems can be seen as metaphors.
You can follow Dr. Rodriguez Hertz on Twitter. You can find more information about the mathematicians and theorems featured in this podcast, along with other delightful mathematical treats, at kpknudson.com and here at Roots of Unity. A transcript is available here. You can subscribe to and review the podcast on iTunes and other podcast delivery systems. We love to hear from our listeners, so please drop us a line at myfavoritetheorem@gmail.com. Kevin Knudson’s handle on Twitter is @niveknosdunk, and mine is @evelynjlamb. The show itself also has a Twitter feed: @myfavethm and a Facebook page. Join us next time to learn another fascinating piece of mathematics.
Previously on My Favorite Theorem:
Episode 0: Your hosts' favorite theorems Episode 1: Amie Wilkinson’s favorite theorem Episode 2: Dave Richeson's favorite theorem Episode 3: Emille Davie Lawrence's favorite theorem Episode 4: Jordan Ellenberg's favorite theorem Episode 5: Dusa McDuff's favorite theorem Episode 6: Eriko Hironaka's favorite theorem Episode 7: Henry Fowler's favorite theorem Episode 8: Justin Curry's favorite theorem Episode 9: Ami Radunskaya's favorite theorem Episode 10: Mohamed Omar's favorite theorem Episode 11: Jeanne Clelland's favorite theorem Episode 12: Candice Price's favorite theorem Episode 13: Patrick Honner's favorite theorem Episode 14: Laura Taalman's favorite theorem Episode 15: Federico Ardila's favorite theorem Episode 16: Jayadev Athreya's favorite theorem Episode 17: Nalini Joshi's favorite theorem Episode 18: John Urschel's favorite theorem Episode 19: Emily Riehl's favorite theorem Episode 20: Francis Su's favorite theorem