This article was published in Scientific American’s former blog network and reflects the views of the author, not necessarily those of Scientific American
At the age of 17 he began dissecting corpses from the church graveyard. Between the years 1508 and 1512 he painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in Rome. Michelangelo Buonarroti—known by his first name the world over as the singular artistic genius, sculptor and architect—was also an anatomist, a secret he concealed by destroying almost all of his anatomical sketches and notes. Now, 500 years after he drew them, his hidden anatomical illustrations have been found—painted on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, cleverly concealed from the eyes of Pope Julius II and countless religious worshipers, historians, and art lovers for centuries—inside the body of God.

This is the conclusion of Ian Suk and Rafael Tamargo, in their paper in the May 2010 issue of the scientific journal Neurosurgery. Suk and Tamargo are experts in neuroanatomy at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland. In 1990, physician Frank Meshberger published a paper in the Journal of the American Medical Association deciphering Michelangelo’s imagery with the stunning recognition that the depiction in God Creating Adam in the central panel on the ceiling was a perfect anatomical illustration of the human brain in cross section. Meshberger speculates that Michelangelo surrounded God with a shroud representing the human brain to suggest that God was endowing Adam not only with life, but also with supreme human intelligence. Now in another panel The Separation of Light from Darkness (shown at left), Suk and Tamargo have found more. Leading up the center of God’s chest and forming his throat, the researchers have found a precise depiction of the human spinal cord and brain stem.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Is the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel a 500 year-old puzzle that is only now beginning to be solved? What was Michelangelo saying by construction the voice box of God out of the brain stem of man? Is it a sacrilege or homage?
It took Michelangelo four years to complete the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel. He proceeded from east to west, starting from the entrance of the Chapel to finish above the altar. The last panel he painted depicts God separating light from darkness. This is where the researchers report that Michelangelo hid the human brain stem, eyes and optic nerve of man inside the figure of God directly above the altar.
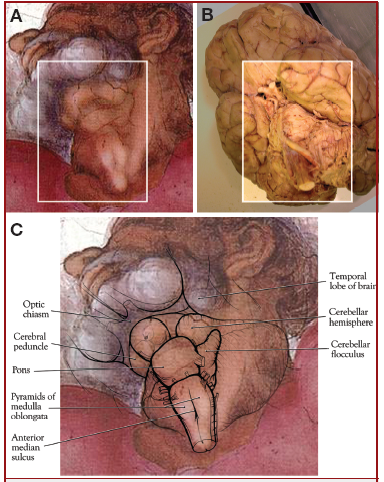
Art critics and historians have long puzzled over the odd anatomical irregularities in Michelangelo’s depiction of God’s neck in this panel, and by the discordant lighting in the region. The figures in the fresco are illuminated diagonally from the lower left, but God’s neck, highlighted as if in a spotlight, is illuminated straight-on and slightly from the right. How does one reconcile such clumsiness by the world’s master of human anatomy and skilled portrayer of light with bungling the image of God above the altar? Suk and Tamargo propose that the hideous goiter-disfigured neck of God is not a mistake, but rather a hidden message. They argue that nowhere else in any of the other figures did Michelangelo foul up his anatomically correct rendering of the human neck. They show that if one superimposes a detail of God’s odd lumpy neck in the Separation of Light and Darkness on a photograph of the human brain as seen from below, the lines of God’s neck trace precisely the features of the human brain [see images at right].
There is something else odd about this picture. A role of fabric extends up the center of God’s robe in a peculiar manner. The clothing is bunched up here as is seen nowhere else, and the fold clashes with what would be the natural drape of fabric over God’s torso. In fact, they observe, it is the human spinal cord, ascending to the brain stem in God’s neck. At God’s waist, the robe twists again in a peculiar crumpled manner, revealing the optic nerves from two eyes, precisely as Leonardo Da Vinci had shown them in his illustration of 1487. Da Vinci and Michelangelo were contemporaries and acquainted with each other’s work.
The mystery is whether these neuroanatomical features are hidden messages or whether the Sistine Chapel a Rorshach tests upon which anyone can extract an image that is meaningful to themselves. The authors of the paper are, after all, neuroanatomists. The neuroanatomy they see on the ceiling may be nothing more than the man on the moon.
But Michelangelo also depicted other anatomical features elsewhere in the ceiling, according to other scholars; notably the kidney, which was familiar to Michelangelo and was of special interest to him as he suffered from kidney stones.
If the hidden figures are intentional, what do they mean? The authors resist speculation, but a great artist does not merely reproduce an object in a work of art, he or she evokes meaning through symbolism. Is Separation of Light from Darkness an artistic comment on the enduring clash between science and religion? Recall that this was the age when the monk Copernicus was denounced by the Church for theorizing that the Earth revolved around the sun. It was a period of struggle between scientific observation and the authority of the Church, and a time of intense conflict between Protestants and Catholics.
It is no secret that Michelangelo’s relationship with the Catholic Church became strained. The artist was a simple man, but he grew to detest the opulence and corruption of the Church. In two places in the masterpiece, Michelangelo left self portraits—both of them depicting himself in torture. He gave his own face to Saint Bartholomew’s body martyred by being skinned alive, and to the severed head of Holofernes, who was seduced and beheaded by Judith.
Michelangelo was a devout person, but later in life he developed a belief in Spiritualism, for which he was condemned by Pope Paul IV. The fundamental tenet of Spiritualism is that the path to God can be found not exclusively through the Church, but through direct communication with God. Pope Paul IV interpreted Michelangelo’s Last Judgment, painted on the wall of the Sistine Chapel 20 years after completing the ceiling, as defaming the church by suggesting that Jesus and those around him communicated with God directly without need of Church. He suspended Michelangelo’s pension and had fig leaves painted over the nudes in the fresco. According to the artist’s wishes, Michelangelo’s body is not buried on the grounds of the Vatican, but is instead interred in a tomb in Florence.
Perhaps the meaning in the Sistine Chapel is not of God giving intelligence to Adam, but rather that intelligence and observation and the bodily organ that makes them possible lead without the necessity of Church directly to God. The material is rich for speculation and the new findings will doubtlessly spark endless interpretation. We may never know the truth, but in Separation of Light from Darkness, Michelangelo’s masterpiece combines the worlds of art, religion, science, and faith in a provocative and awe inspiring work of art, which may also be a mirror.
Images from "Concealed Neuroanatomy in Michelangelo’s Separation of Light From Darkness in the Sistine Chapel," by Ian Suk and Rafael J. Tamargo in Neurosurgery, Vol. 66, No. 5, pp. 851-861.
5/27/10: Typographical errors were corrected thanks to readers' comments.